In this tutorial you will learn about the C Program to Copy a File and its application with practical example.
C Program to Copy a File
In this tutorial, you will learn about the C Program to Copy a File with a practical example.
Prerequisites
Before starting with this tutorial we assume that you are best aware of the following C programming topics:
- Operators in C Programming.
- Basic Input and Output function in C Programming.
- Basic C programming.
- Concepts of while loop.
- Conditional Statements in C programming.
- Using file functions of c language.
Program to Copy a File
As we all know the file is a collection of characters, integers, and many data types. In strings, only one variable is declared which can store multiple values. First will take the file from the user. Then will Check that file if it’s empty or not. The C programming language has many pre-defined functions for file manipulation. but in today’s tutorial, we will Copy a File.
With the help of this program, we can Copy a File
Algorithm:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
1. Declaring the variables for the program. 2. Taking the input from the user. 3. Reading the file. 4. <strong>Copy a File </strong>if there is any data in it. 5. Printing the results ouput message. 6. End program. |
Program:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
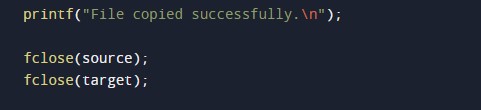
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main() { //declaring the variables for the program char ch, source_file[20], target_file[20]; FILE *source, *target; //taking input file from the user to copy printf("Enter name of file to copy\n"); gets(source_file); source = fopen(source_file, "r"); if (source == NULL) { printf("Press any key to exit...\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } //Printing the output for the program printf("Enter name of target file\n"); gets(target_file); target = fopen(target_file, "w"); if (target == NULL) { fclose(source); printf("Press any key to exit...\n"); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while ((ch = fgetc(source)) != EOF) fputc(ch, target); //output message for successful copy of the file printf("File copied successfully.\n"); fclose(source); fclose(target); return 0; } |
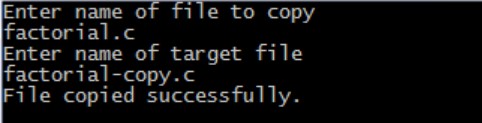
Output:-
In the above program, we have first initialized the required variable.
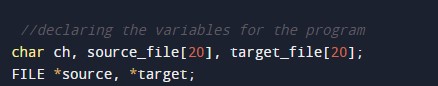
- *source = it will hold the address value.
- *target = it will hold the new file data.
Taking input file name.
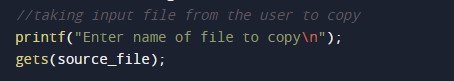
Reading the file and taking the target file.
Copying the file.
Printing the output.