In this tutorial you will learn about the C program to implement MERGE sort Algorithm and its application with practical example.
C Program to Merge sort Algorithm
In this tutorial, we will learn to create a C program that will do Merge sort using C programming.
Prerequisites
Before starting with this tutorial we assume that you are best aware of the following C programming topics:
- Operators in C Programming.
- Basic Input and Output function in C Programming.
- Basic C programming.
- While loop in C programming.
- For loop in C Programming.
- Creating and Using the user-defined function in C programming.
What is Merge Sort?
In every programming language, the sorting of data is a very important factor. In C Language. Many different techniques for sorting are available to work with but in this tutorial, we will focus on the Merge Sort Technique.
In this technique, we will divide the array into smaller chunks until there is only one element left. Then we will merge the chunks and gets a sorted array.
Algorithm
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
MERGE_SORT(arr, beg, end) if beg < end set mid = (beg + end)/2 MERGE_SORT(arr, beg, mid) MERGE_SORT(arr, mid + 1, end) MERGE (arr, beg, mid, end) end of if END MERGE_SORT |
Program For Merge Sort
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 |
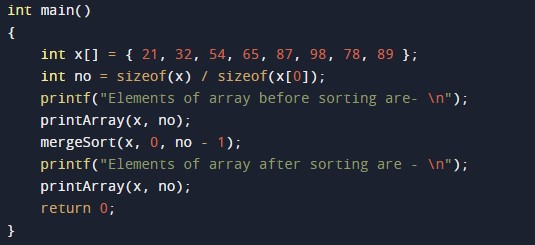
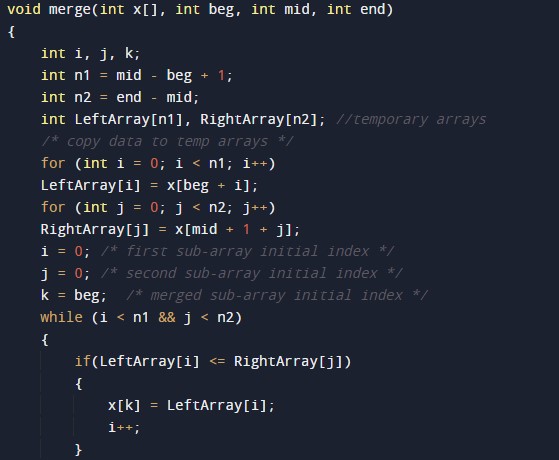
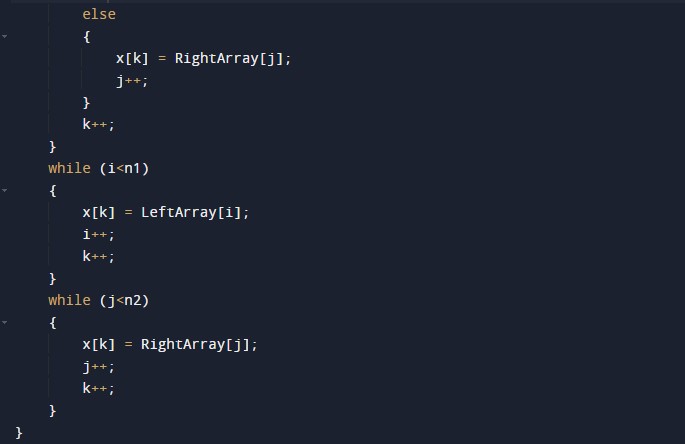
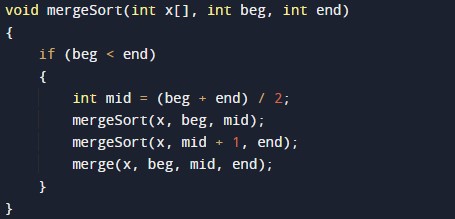
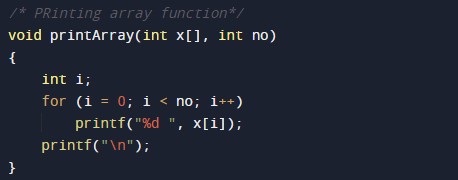
#include <stdio.h> /* Merging Sub array of x[] */ void merge(int x[], int beg, int mid, int end) { int i, j, k; int n1 = mid - beg + 1; int n2 = end - mid; int LeftArray[n1], RightArray[n2]; //temporary arrays /* copy data to temp arrays */ for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++) LeftArray[i] = x[beg + i]; for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++) RightArray[j] = x[mid + 1 + j]; i = 0; /* first sub-array initial index */ j = 0; /* second sub-array initial index */ k = beg; /* merged sub-array initial index */ while (i < n1 && j < n2) { if(LeftArray[i] <= RightArray[j]) { x[k] = LeftArray[i]; i++; } else { x[k] = RightArray[j]; j++; } k++; } while (i<n1) { x[k] = LeftArray[i]; i++; k++; } while (j<n2) { x[k] = RightArray[j]; j++; k++; } } void mergeSort(int x[], int beg, int end) { if (beg < end) { int mid = (beg + end) / 2; mergeSort(x, beg, mid); mergeSort(x, mid + 1, end); merge(x, beg, mid, end); } } /* PRinting array function*/ void printArray(int x[], int no) { int i; for (i = 0; i < no; i++) printf("%d ", x[i]); printf("\n"); } int main() { int x[] = { 21, 32, 54, 65, 87, 98, 78, 89 }; int no = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]); printf("Elements of array before sorting are- \n"); printArray(x, no); mergeSort(x, 0, no - 1); printf("Elements of array after sorting are - \n"); printArray(x, no); return 0; } |
Output:-
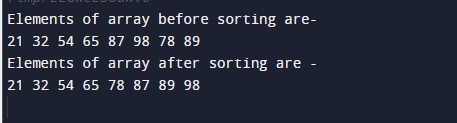
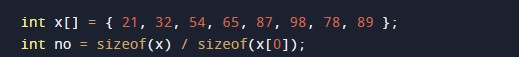
In the above program, we have first declared and initialized a set variables required in the program.
- no = it will hold the size of array.
- x[]= it will hold the elements in a array.
Subarray sorting merging Function Body:-
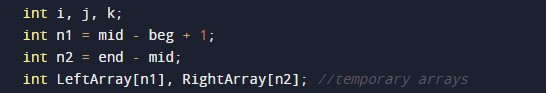
- i = it will hold the integer value to control the array.
- j = it will hold the integer value to control the array.
- k= it will hold the integer value to control the array.
- LeftArray = it will hold the left array values.
- RightArray = it will hold the left array values.
Merge Sorting Function Body:-
Print Array Function body:-
The main function to perform and navigate the program cleanly.