In this tutorial you will learn about the C Program to implement Selection sort Algorithm and its application with practical example.
C Program to implement Selection Sort Algorithm
In this tutorial, we will learn to create a C program that will do Selection sorting using C programming.
Prerequisites
Before starting this tutorial we assume that you are best aware of the following C programming topics:-
- Operators in C Programming.
- Basic Input and Output function in C Programming.
- Basic C programming.
- For loop in C Programming.
- Creating and Using the user-define function in C programming.
What is Selection Sort?
In every programming language, the sorting of data is a very important factor. In C Language. Many different techniques for sorting are available to work with but in this tutorial, we will focus on the Selection Sort Technique.
It’s the most simple sorting technique. In this technique, we will select the smallest array element and place it in the first position the second on the second position.
Algorithm
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
SELECTION SORT(arry, n) Step 1: Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for i = 0 to n-1 Step 2: CALL SMALLEST(arry, i, n, pos) Step 3: SWAP arry[i] with arry[pos] [END OF LOOP] Step 4: EXIT SMALLEST (arry, i, n, pos) Step 1: [INITIALIZE] SET SMALL = arry[i] Step 2: [INITIALIZE] SET pos = i Step 3: Repeat for j = i+1 to n if (SMALL > arry[j]) SET SMALL = arry[j] SET pos = j [END OF if] [END OF LOOP] Step 4: RETURN pos |
Program For Selection Sort
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 |
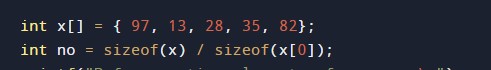
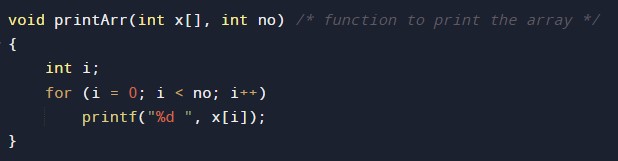
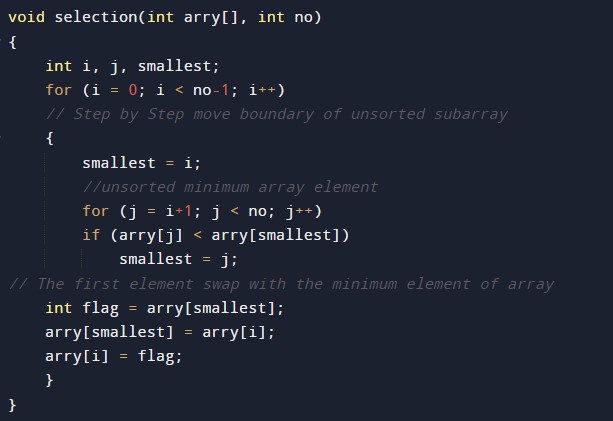
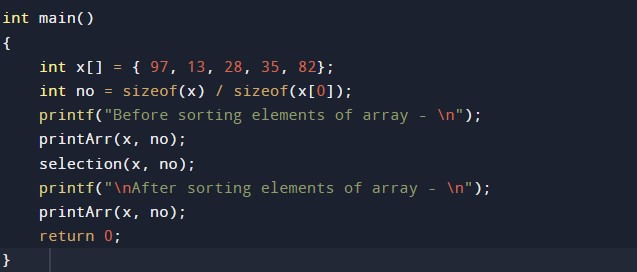
#include <stdio.h> void selection(int arry[], int no) { int i, j, smallest; for (i = 0; i < no-1; i++) // Step by Step move boundary of unsorted subarray { smallest = i; //unsorted minimum array element for (j = i+1; j < no; j++) if (arry[j] < arry[smallest]) smallest = j; // The first element swap with the minimum element of array int flag = arry[smallest]; arry[smallest] = arry[i]; arry[i] = flag; } } void printArr(int x[], int no) /* function to print the array */ { int i; for (i = 0; i < no; i++) printf("%d ", x[i]); } int main() { int x[] = { 97, 13, 28, 35, 82}; int no = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]); printf("Before sorting elements of array - \n"); printArr(x, no); selection(x, no); printf("\nAfter sorting elements of array - \n"); printArr(x, no); return 0; } |
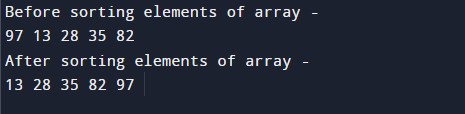
Output:-
In the above program, we have first declared and initialized a set of variables required in the program.
- no = it will hold the size of the array.
- x[]= it will hold the elements in an array.
- flag= it will hold the temporary values.
- i= it will hold the integer value to control the array.
- j= it will hold the integer value to control the array.
Function to print on the terminal/console.
Function to implement the bubble sort.
The main function to perform and navigate the program cleanly.