In this tutorial you will learn about the C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on One Dimensional Array and its application with practical example.
C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on One Dimensional Array
In this tutorial, we will learn to create a C program that will Perform Arithmetic Operations on One Dimensional Array using C programming.
Prerequisites
Before starting with this tutorial, we assume that you are the best aware of the following C programming topics:
- Operators in C Programming.
- Basic Input and Output function in C Programming.
- Basic C programming.
- For loop in C programming.
- Arithmetic operations in C Programming.
Algorithm:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
STEP 1: START STEP 2: INITIALIZE array size and elements STEP 3: Performing the arithmetic operations on the array STEP 4: PRINT the array results. STEP 5: RETURN 0. STEP 6: END PROGRAM |
What is An array?
The array is a collection of similar data types. An array can store multiple values with different indexes in memory by using a single variable.
Perform Arithmetic Operations on One Dimensional Array.
In this program, First, we will first take the size of the arrays from the user. Then we will take the elements of the array 1 and 2 from the user. After that, we will perform the arithmetic operations on the elements for the array. Then we will print the results of that array.
With the help of this program, we can Perform Arithmetic Operations on One Dimensional Array.
Program Code:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 |
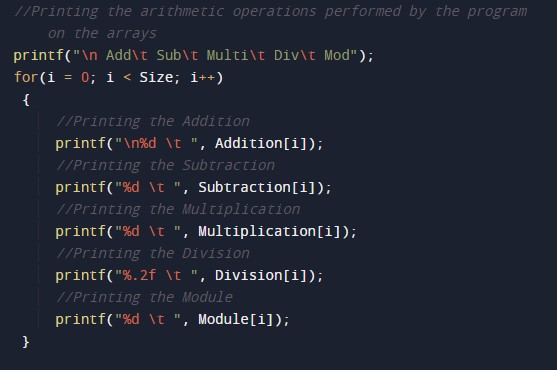
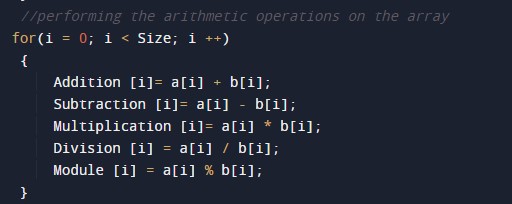
/* C Program to Perform Arithmetic Operations on One Dimensional Array */ #include<stdio.h> int main() { //declaring the required variable for the int Size, i, a[10], b[10]; int Addition[10], Subtraction[10], Multiplication[10], Module[10]; float Division[10]; //Taking the size of the array printf("\n Please Enter the Size of the Array\n"); scanf("%d", &Size); //taking the elements of the first array printf("\nPlease Enter the First Array Elements\n"); for(i = 0; i < Size; i++) { scanf("%d", &a[i]); } //Taking the elements of the second array printf("\n Please Enter the Second Array Elements\n"); for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++) { scanf("%d", &b[i]); } //performing the arithmetic operations on the array for(i = 0; i < Size; i ++) { Addition [i]= a[i] + b[i]; Subtraction [i]= a[i] - b[i]; Multiplication [i]= a[i] * b[i]; Division [i] = a[i] / b[i]; Module [i] = a[i] % b[i]; } //Printing the arithmetic operations performed by the program on the arrays printf("\n Add\t Sub\t Multi\t Div\t Mod"); for(i = 0; i < Size; i++) { //Printing the Addition printf("\n%d \t ", Addition[i]); //Printing the Subtraction printf("%d \t ", Subtraction[i]); //Printing the Multiplication printf("%d \t ", Multiplication[i]); //Printing the Division printf("%.2f \t ", Division[i]); //Printing the Module printf("%d \t ", Module[i]); } return 0; } |
Output:-
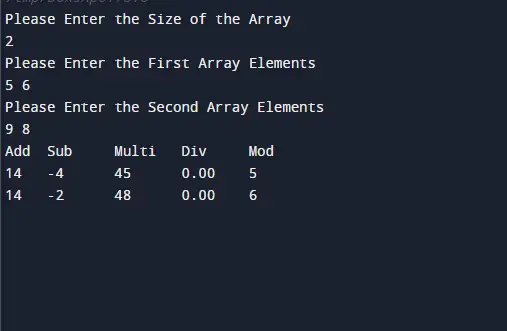
In the above program, we have first initialized the required variable.
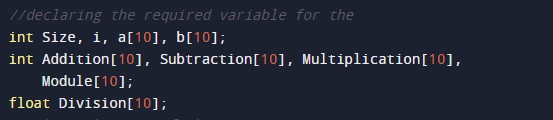
- Size = it will hold the integer value.
- i = it will hold the integer value.
- a[10] = it will hold the integer value.
- b[10] = it will hold the integer value.
Taking the size and elements of the arrays.
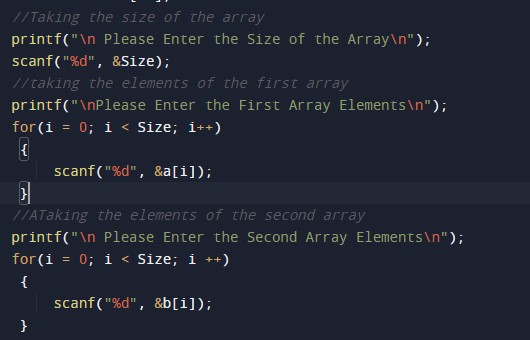
Program Logic Code.
Printing output of the program.