C Recursion
In C programming, recursion is a process where a function calls itself to solve a complex iterative task. The function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. The recursive function calls itself to solve a complex iterative task by dividing it into sub-tasks. In this tutorial, you’ll learn about recursion in C. In particular, you’ll learn:
- What Is Recursion
- What Is Recursive Function
- Working Of Recursive Function
- Recursion flowchart
- Characteristics of a Recursive function
- Advantages Of Recursion
- Disadvantages Of Recursion
What Is Recursion In C
Recursion is the process where a function calls itself its subroutine in order to solve a complex iterative task by dividing it into sub-tasks. The function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. Any function which calls itself recursively is called a recursive function. The process of calling a function by itself is called recursion. It is an efficient approach to solving a complex mathematical computation task by dividing it into sub-tasks. The approach to solving a problem in recursion is called Divide and Conquer.
Any problem that can be solved recursively, can also be solved iteratively but recursion is considered a more efficient method of programming. It requires the least amount of code to perform some complex tasks using recursion instead of another method. Although recursion is not recommended for all problems, it is best suited for some problems like sorting, searching, Inorder/Preorder/Postorder Tree Traversals, DFS of Graph algorithms. However, recursion must be implemented carefully. Otherwise, it may lead to an infinite loop if no base condition is met that will terminate the function.
What Is Recursive Function
Any function which calls itself recursively is called a recursive function. A recursive function calls itself to solve a complex iterative task by dividing it into sub-tasks. A recursive function repeats itself several times to compute or return the final output. Recursion must be implemented carefully otherwise it may lead to an infinite loop. The recursive function must have a valid terminating condition or base case that will terminate the function. At this point, recursion stops, and the final result is returned from the function.
Syntax Of Recursive Function In C
The general pseudocode representation or syntax of a recursive function in c programming is as follows:
Syntax:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
void recurse() { recursion(); /* function calls itself */ } int main() { recurse(); return 0; } |
Characteristics of a recursive function In C
The General Characteristics of a recursive function is as follows:
- A recursive function is a function that calls itself.
- The speed of a recursive program is slower because of stack overheads.
- A recursive function must have terminating conditions and recursive expressions.
Note:- Recursive function must have a valid terminating condition otherwise it leads to an infinite loop.
How does recursion work In C?
To understand how recursion works let’s have one of the popular examples of recursion. In this example, we will calculate the factorial of n numbers. The factorial of n numbers is expressed as a series of repetitive multiplication as shown below:
|
1 |
Factorial of n (n!) = n*(n-1)*(n-2)...1 |
Suppose we want to find a factorial of 5, then this will be represented as following using recursion:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
f = 5*factorial(5-1); f = 5*4*factorial(4-1); f = 5*4*3*factorial(3-1); f = 5*4*3*2*factorial(2-1); f = 5*4*3*2*1; f = 120; |
The flowchart image illustrates the working of recursive function to find factorial of 5 :
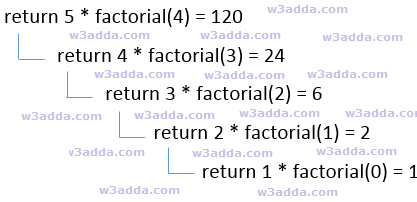
Here, the recurse() function is a recursive function. It calls itself inside the functional body.
Factorial Program in C Using Recursion
The following factorial program demonstrates the use of the recursive function to find the factorial of a given number using recursion in c programming.
Program:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int factorial(int); int factorial(int i) { int f; if(i==1) return 1; else f = i* factorial (i-1); return f; } void main() { int x; clrscr(); printf("Enter any number to calculate factorial :"); scanf("%d",&x); printf("\nFactorial : %d", factorial (x)); getch(); } |
Output:-
|
1 2 |
Enter any number to calculate factorial :5 Factorial : 120 |
Suppose the value of i=5, since i is not equal to 1, the statement:
|
1 |
f = i*factorial(i-1); |
will be executed with i=5 i.e.
|
1 |
f = 5* factorial(5-1); |
As you can see this statement again calls a factorial function with value i-1 which will return the value:
|
1 |
4*factorial4-1); |
This recursive calling process continues until the value of i is equal to 1. When i is equal to 1 it returns 1 and execution of this function stops. We can review the series of recursive call as follow:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
f = 5*factorial(5-1); f = 5*4*factorial(4-1); f = 5*4*3*factorial(3-1); f = 5*4*3*2*factorial(2-1); f = 5*4*3*2*1; f = 120; |
Fibonacci Series In C Using Recursion
The following Fibonacci series program demonstrates the use of the recursive function to generate the Fibonacci series of a given number using recursion in c programming.
Program:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int fibonacci(int g) { if (g == 0) { return 0; } if (g == 1) { return 1; } return fibonacci(g - 1) + fibonacci(g - 2); } int main(void) { int g; printf("Fibonacci Series As Follows:\n"); for (g = 0; g < 10; g++) { printf("%d \t ", fibonacci(g)); } getch(); return 0; } |
Output:-
|
1 2 |
Fibonacci Series As Follows: 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 |
Advantages of Recursion In C
Advantages of recursion are as follows:
- It requires a few variables which make the program clean.
- It shortens the complex and nested code.
Disadvantages of Recursion In C
Disadvantages of recursion are as follows:
- It is hard to debug the recursive functions.
- It is tough to understand the logic of a recursive function.
