In this tutorial you will learn about the C++ Variable Scope and its application with practical example.
C++ Variable Scope
What Is Variable Scope?
Scope defines the region of visibility or availability for a variable, out of which we can not reference that variable. In C++, variable declared inside main() function can not be accessed outside the main() function. Scope of a variable is limited to the curly braces containing it, if you try to access that variable outside those curly braces then you will get compilation error. In C++, variables can be of following two types based on their scope.
- Global Variables
- Local Variables
C++ Global Variable
Global variables can be accessed at any point throughout the program, and can be used in any function. There is single copy of the global variable is available. Global variables are defined outside of all the functions, usually on top of the main() function.
Example:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // This is a global variable char globalVar = 'G'; int main() { cout<<"W3Adda - C++ Global Variable"<<endl; cout <<"Value of globalVar: "<< globalVar<<endl; globalVar='A';// Value of global variable changed cout <<"Value of globalVar: "<< globalVar; return 0; } |
Output:-
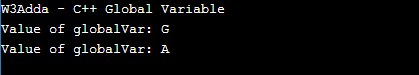
C++ Local Variable
Variable declared inside a function or block of code are called local variables. They can be accessed only inside that function or block of code. Local variables are not available outside the function it is defined in.
Example:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 |
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // This is a global variable char funA(){ char a = 'A'; cout<<"Value of a inside funA is: "<< a<<endl; } char funB(){ char a = 'B'; cout<<"Value of a inside funB is: "<< a<<endl; } int main() { char a = 'M'; cout<<"W3Adda - C++ Local Variable"<<endl; funA(); funB(); cout<<"Value of a inside Main is: "<< a<<endl; return 0; } |
Output:-
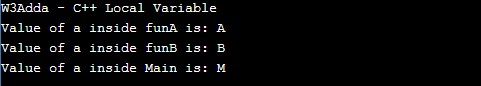
Note :- A program can have same name for local and global variables but local variable overrides the value.

