In this tutorial you will learn about the Merge Sort Algorithm and its application with practical example.
Merge Sort Program In C
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 |
#include<stdio.h> void mergesort(int a[],int i,int j); void merge(int a[],int i1,int j1,int i2,int j2); int main() { int nums[30],n,i; printf("Enter no of elements:"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("Enter %d integer numbers\n", n); for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&nums[i]); mergesort(nums,0,n-1); printf("Elements after sorting: "); for(i=0;i<n;i++) printf("%d ",nums[i]); return 0; } void mergesort(int a[],int i,int j) { int mid; if(i<j) { mid=(i+j)/2; mergesort(a,i,mid); //left recursion mergesort(a,mid+1,j); //right recursion merge(a,i,mid,mid+1,j); //merging of two sorted sub-arrays } } void merge(int a[],int i1,int j1,int i2,int j2) { int temp[50]; //array used for merging int i,j,k; i=i1; //beginning of the first list j=i2; //beginning of the second list k=0; while(i<=j1 && j<=j2) //while elements in both lists { if(a[i]<a[j]) temp[k++]=a[i++]; else temp[k++]=a[j++]; } while(i<=j1) //copy remaining elements of the first list temp[k++]=a[i++]; while(j<=j2) //copy remaining elements of the second list temp[k++]=a[j++]; //Transfer elements from temp[] back to a[] for(i=i1,j=0;i<=j2;i++,j++) a[i]=temp[j]; } |
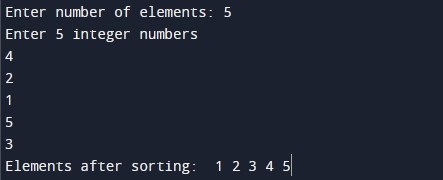
Output:-