In this tutorial you will learn about the R Environment and its application with practical example.
R Environment
In R, as soon as R interpreter is started a run time environment is automatically created. This run time environment holds up a collection of all run-time entities being created including functions, variables etc.
R Global Environment
The top level environment, when the R interpreter is started is termed as global environment. This can be referred to as .GlobalEnv in R program, a
R ls() function
In R, ls() function is used to list all of the variables and functions available in current environment.
Example:-

R environment() function
The environment() function is used to show current environment.
Example:-

R Environments Cascading
In R, whenever a new function is defined, a new environment is created for it. An environment actually has a frame, that contains all of the entities being defined, it also contains a pointer to its enclosing (parent) environment. In R, defining a function inside another function results in cascading of environment.
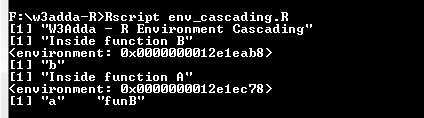
Example:-
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
funA <- function(a){ funB <- function(b){ print("Inside function B") print(environment()) print(ls()) } funB(5) print("Inside function A") print(environment()) print(ls()) } print("W3Adda - R Environment Cascading") funA(10) |
Here, we have function named funA which is accepting a parameter “a”, inside this we have function named funB which accepting parameter “b”.
Let’s run the above program to see the output –
Output:-